Source: Global Population Growth Is Slowing Down. Here’s One Reason Why – Scientific American
…
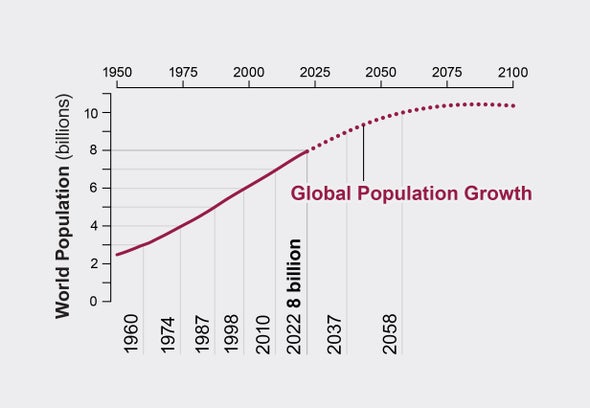
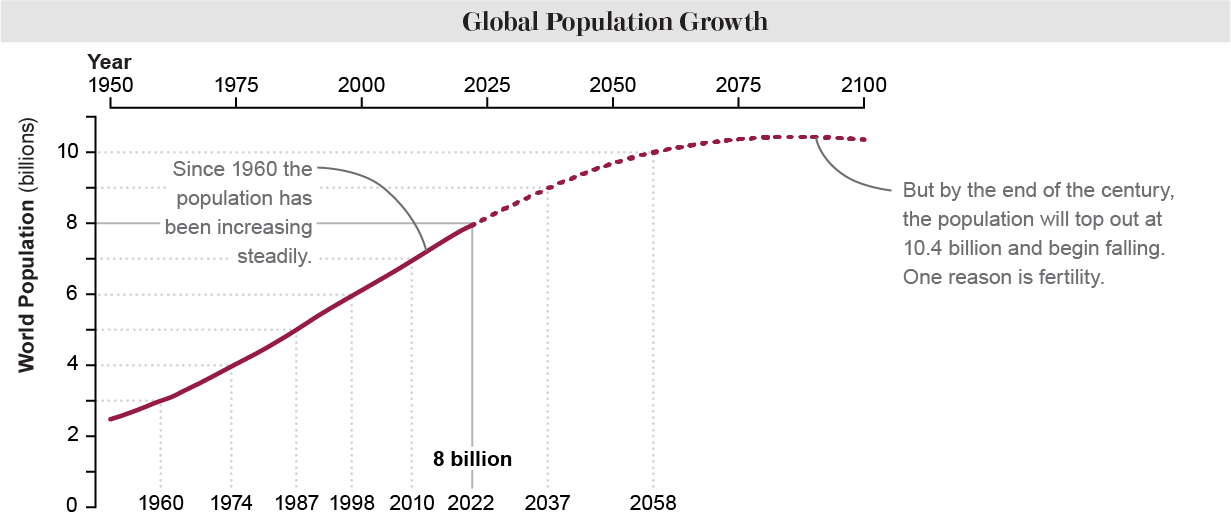
On November 15, 2022—as estimated by demographers—the count of humans on this planet reached eight billion. Population growth has been steady over the past few decades, with billion-person marks coming every dozen years or so. But that pattern is changing. Growth is beginning to slow, and experts predict the world’s population will top out sometime in the 2080s at about 10.4 billion.
That slowdown is partly the result of a shift toward fewer offspring—a phenomenon that is happening almost everywhere around the world, though at different rates. High-income nations now have the lowest birth rates, and the lowest-income nations currently have the highest birth rates. “The gap has continued to widen between wealthy nations and poorer ones,” says Jennifer Sciubba, a social scientist at the Wilson Center in Washington, D.C., who has written about these planetary-scale demographic shifts. “But longer term,” she says, “we’re moving toward convergence.” In other words, this disparity among nations’ birth rates isn’t a permanent chasm. It’s a temporary divide that will narrow over the coming decades.
Many factors contribute to the waxing and waning of the world’s population, such as migration, mortality, longevity and other major demographic metrics. Focusing on fertility, however, helps to illuminate why the total number of humans on Earth seems set to fall. Demographers define fertility as the average total number of live births per female individual in a region or country. (In the accompanying graphics, the term “woman” is used to encompass anyone assigned female at birth.) The U.S.’s present fertility rate, for example, is about 1.7; China’s is 1.2. Demographers consider a fertility rate of 2.1 to be the replacement rate—that is, the required number of offspring, on average, for a population to hold steady. Today birth rates in the wealthiest countries are below the replacement rate. About 50 percent of all nations fall below the replacement rate, and in 2022 the region with the lowest fertility rate (0.8) was Hong Kong. Over the coming decades most of the rest of the world’s countries will likely follow suit.
Leave a Reply